코드 품질 관리에 대하여
목차
일관성 있는 코드를 유지하고 일정 수준 이상의 품질을 보장하기 위해 도입했어요.
도구 선택
SonarQube(올인원)와 개별 도구 조합을 비교했어요. SonarQube는 대시보드와 이력 관리가 편하지만, SonarCloud는 private 레포에서 유료이고 SonarQube 셀프호스팅은 3GB+ RAM이 필요합니다. 1인 개발에 private 레포로 운영하는 상황에서 무료로 쓸 수 있는 개별 도구 조합(Spotless + Checkstyle + SpotBugs + JaCoCo + Codecov)을 선택했어요.
선택한 도구들
1. Spotless - 코드 포맷팅
역할: 코드 스타일 자동 통일
IDE 포맷터나 EditorConfig만으로는 Java의 import 순서, 중괄호 위치 같은 언어별 규칙까지 통일하기 어려워요. Spotless는 Google Java Format을 Gradle 빌드에 통합해서 CI에서 자동 검증하고, 로컬에서 ./gradlew spotlessApply 한 번으로 자동 수정됩니다.
동작 방식:
# 포맷팅 검사 (CI에서 실행)./gradlew spotlessCheck
# 자동 포맷팅 (로컬에서 실행)./gradlew spotlessApply설정 (build.gradle.kts):
2. Checkstyle - 코딩 컨벤션
역할: 코딩 규칙 준수 검사
SpotBugs는 바이트코드 분석으로 버그 패턴을 찾고, Checkstyle은 소스코드에서 코딩 컨벤션을 검사해요. 역할이 다르므로 둘 다 사용합니다. PMD(코드 복잡도, 중복 코드 탐지)는 SpotBugs가 일부 역할을 대체하므로 제외했어요. Google Java Style Guide 기반 규칙을 적용하고, suppressions 파일로 특정 클래스를 예외 처리할 수 있습니다.
주요 검사 항목:
- 네이밍 규칙 (camelCase, CONSTANT_CASE)
- import 규칙 (star import 금지, 사용하지 않는 import)
- 블록 규칙 (중괄호 필수, 빈 블록 금지)
- 메서드 길이 (50줄 제한)
- 파라미터 개수 (7개 제한, 생성자 제외)
Star Import(import .*) 금지 이유
왜 금지하는가?
네임스페이스 충돌
java.util.Date와 java.sql.Date를 동시에 star import하면 Date 클래스가 어느 패키지인지 모호해져요. 컴파일러가 에러를 내거나, 의도하지 않은 클래스가 사용될 수 있습니다.
의존성 불명확
코드만 보고 어떤 클래스를 실제로 사용하는지 파악할 수 없어요. 코드 리뷰나 디버깅 시 불편합니다.
라이브러리 업그레이드 위험
라이브러리 새 버전에서 추가된 클래스가 기존 코드의 클래스명과 충돌할 수 있어요. 명시적 import는 이 위험을 방지합니다.
예외: 테스트 코드의 static import는 가독성을 위해 허용하기도 함
Suppressions: DTO, Entity, Config, Test 클래스는 일부 규칙을 완화했어요. 이들은 구조적으로 많은 필드나 긴 설정을 가질 수밖에 없기 때문이에요.
3. SpotBugs - 버그 탐지
역할: 잠재적 버그 패턴 탐지
FindBugs가 2015년 이후 업데이트가 중단되어 그 후속인 SpotBugs를 선택했어요. Google의 Error Prone(컴파일 타임 버그 탐지)도 검토했지만, Gradle 설정이 복잡하고 SpotBugs가 더 많은 버그 패턴을 탐지합니다. 바이트코드 분석으로 소스코드만으로는 찾기 어려운 버그를 잡아줘요.
탐지하는 버그 유형:
- Null 포인터 역참조 가능성
- 리소스 누수 (스트림, 커넥션)
- 동시성 문제
- 성능 안티패턴
- 보안 취약점
설정:
Exclude 설정: DTO, Entity의 getter가 가변 객체를 반환하는 경고(EI_EXPOSE_REP)는 의도된 동작이므로 제외했어요.
4. JaCoCo - 테스트 커버리지
역할: 코드 커버리지 측정 및 검증
Cobertura는 2015년 이후 업데이트가 느려졌고, IntelliJ 내장 커버리지는 IDE에서만 확인 가능해요. JaCoCo는 Eclipse Foundation에서 관리하면서 최신 Java 버전을 빠르게 지원하고, Gradle 통합과 Codecov 연동이 잘 되어 CI 자동화에 적합합니다.
커버리지 기준:
왜 60%/70%인가?
40% 미만은 테스트가 거의 없는 상태고, 60%면 핵심 비즈니스 로직은 테스트된 상태로 초기 프로젝트에서 현실적인 목표예요. 80%면 대부분의 코드가 테스트된 안정화 단계이고, 100%는 getter/setter까지 모두 테스트해야 하므로 ROI가 낮아 현실적이지 않습니다.
5. Codecov - 커버리지 대시보드
역할: 커버리지 시각화 및 이력 관리
Coveralls도 무료 커버리지 대시보드를 제공하지만, Codecov가 PR 코멘트가 더 깔끔하고 GitHub Actions 통합이 쉬워요. SonarCloud는 private 레포에서 유료이고, 이미 개별 도구를 쓰고 있어서 커버리지 대시보드만 필요했습니다. Codecov는 개인 프로젝트 무료이고 JaCoCo XML 리포트를 업로드하면 바로 동작해요.
Codecov vs Coveralls 실제 비교
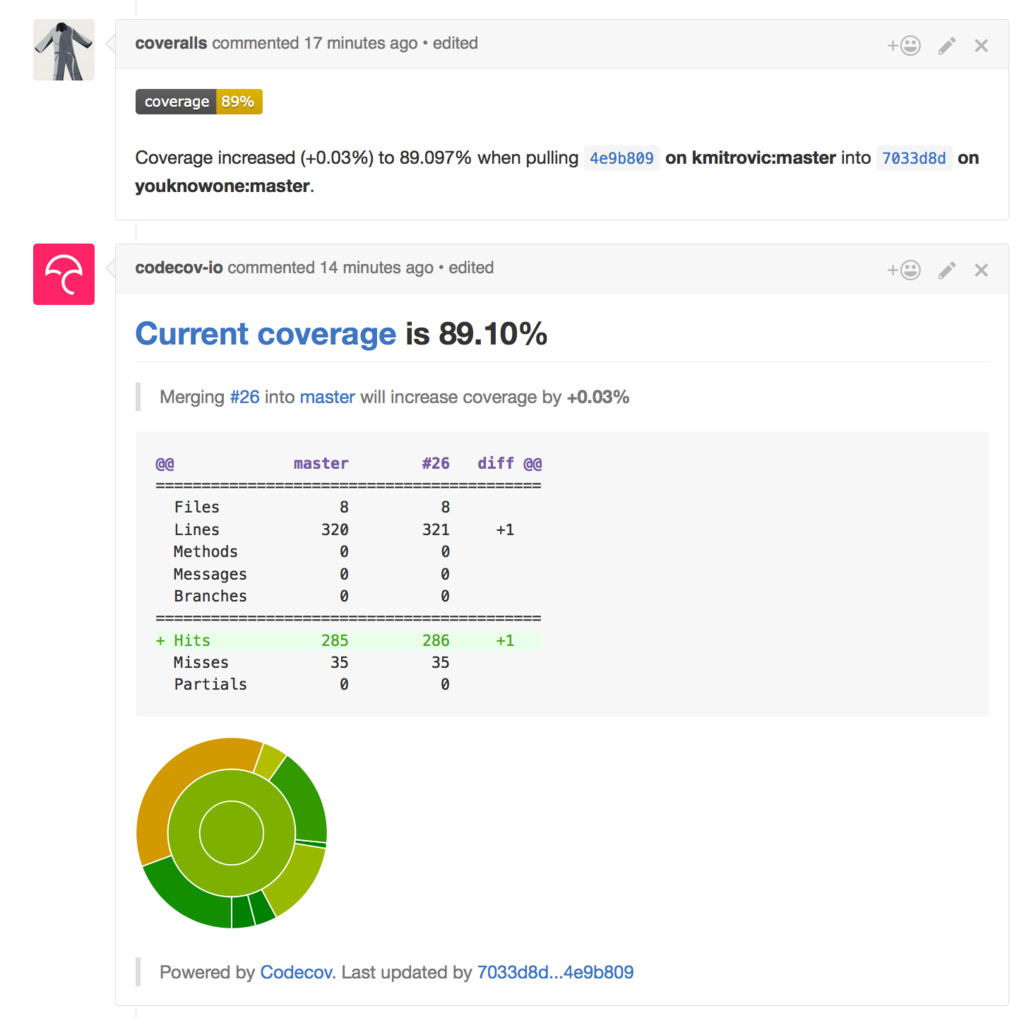
위 이미지에서 중요한 차이가 보여요. Codecov는 비율이 아닌 정확한 줄 수로 표시하고, 패치 밖에서 바뀐 커버리지 여부와 패치 안의 코드 커버리지를 구분해서 보여줍니다.
Coveralls는 커버리지가 올랐는지 내렸는지만 보여줘서 숫자 게임처럼 느껴져요. 실제로 패치가 모두 커버되는지 확인하려면 웹사이트에 직접 방문해야 합니다. 반면 Codecov는 PR 코멘트에서 패치에 대한 상세 정보를 바로 확인할 수 있어요.
Codecov 제공 기능:
- PR별 커버리지 변화 시각화
- 커버리지 트렌드 그래프
- 파일/디렉토리별 커버리지 맵
- Slack/GitHub 통합
가격 정책:
- Public 레포: 무료
- Private 레포 (1~5명): 무료
- Private 레포 (6명 이상): 유료 플랜
private 레포이지만 혼자 만들고 있으니 무료 범위에 해당해요.
참고: Codecov Pricing
설정 방법:
- codecov.io에서 GitHub 연동
- Repository Settings > Secrets에
CODECOV_TOKEN추가 (Private 레포는 토큰 필수) codecov.yml로 세부 설정
codecov.yml 파일 위치:
모노레포 구조에서 codecov.yml은 반드시 레포지토리 루트에 위치해야 해요. backend/ 폴더에 넣으면 인식되지 않습니다.
- 허용 위치:
/,/dev/,/.github/ - 서브 디렉토리 (예:
/backend/)에는 배치 불가
CI 파이프라인 구조
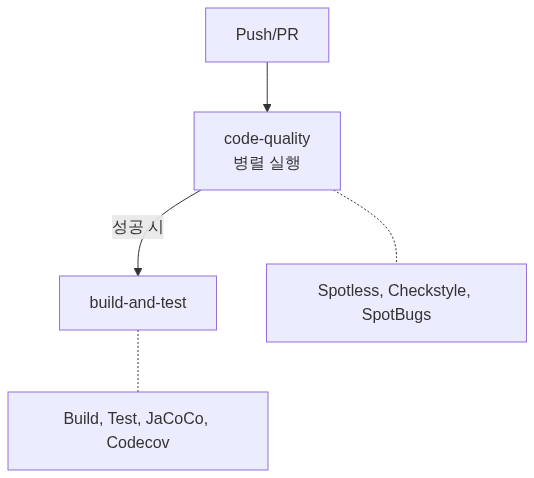
단계 분리 이유:
- 코드 품질 검사가 빠르게 실패하면 빌드 시간 절약
- 어느 단계에서 문제인지 명확히 파악 가능
로컬 개발 워크플로우
커밋 전 검사
# 포맷팅 자동 적용./gradlew spotlessApply
# 전체 검사 (CI와 동일)./gradlew checkIDE 설정 권장
IntelliJ IDEA:
- File > Settings > Editor > Code Style > Java
- Scheme 옆 톱니바퀴 > Import Scheme > Google Style
주요 Gradle 태스크
| 태스크 | 설명 |
|---|---|
spotlessCheck | 포맷팅 검사 |
spotlessApply | 포맷팅 자동 적용 |
checkstyleMain | 메인 코드 Checkstyle |
checkstyleTest | 테스트 코드 Checkstyle |
spotbugsMain | 메인 코드 SpotBugs |
test | 테스트 실행 |
jacocoTestReport | 커버리지 리포트 생성 |
jacocoTestCoverageVerification | 커버리지 기준 검증 |
check | 위 모든 검사 실행 |
버전 호환성 (Java 25 + Spring Boot 4)
| 도구 | 버전 | Java 25 지원 | 비고 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring Boot | 4.0.1 | O | Java 17~25 공식 지원 |
| Spotless | 7.0.2 | O | Google Java Format |
| Checkstyle | 12.3.0 | O | 10.x는 Java 22까지만 지원 |
| SpotBugs Plugin | 6.4.8 | O | 6.0.x는 Java 25 미지원 |
| SpotBugs Annotations | 4.9.8 | O | |
| JaCoCo | 0.8.14 | O | 0.8.12는 Java 22까지만 지원 |
Java 25 LTS를 사용하려면 위 버전 이상을 사용해야 해요.
비용 요약
| 도구 | 비용 | 비고 |
|---|---|---|
| Spotless | 무료 | Gradle 플러그인 |
| Checkstyle | 무료 | Gradle 내장 |
| SpotBugs | 무료 | Gradle 플러그인 |
| JaCoCo | 무료 | Gradle 내장 |
| Codecov | 무료 | 개인/오픈소스 무료 |
| GitHub Actions | 무료 | Private 레포 2000분/월 |
총 비용: $0
참고 자료
- Google Java Style Guide
- Spotless Gradle Plugin
- Checkstyle Documentation
- SpotBugs Documentation
- JaCoCo Documentation
- Codecov Documentation
Introduced to maintain consistent code and guarantee a certain level of quality.
Tool Selection
I compared SonarQube (all-in-one) with a combination of individual tools. SonarQube offers a convenient dashboard and history management, but SonarCloud is paid for private repos, and self-hosting SonarQube requires 3GB+ RAM. As a solo developer running a private repo, I chose a free combination of individual tools (Spotless + Checkstyle + SpotBugs + JaCoCo + Codecov).
Selected Tools
1. Spotless - Code Formatting
Role: Automatically unify code style
IDE formatters or EditorConfig alone cannot enforce language-specific rules like Java import ordering or brace placement. Spotless integrates Google Java Format into the Gradle build for automatic CI verification, and locally everything is auto-fixed with a single ./gradlew spotlessApply.
How it works:
# Check formatting (run in CI)./gradlew spotlessCheck
# Auto-format (run locally)./gradlew spotlessApplyConfiguration (build.gradle.kts):
2. Checkstyle - Coding Conventions
Role: Verify coding rule compliance
SpotBugs uses bytecode analysis to find bug patterns, while Checkstyle inspects source code for coding convention violations. Since their roles differ, both are used. PMD (code complexity, duplicate code detection) was excluded because SpotBugs partially covers its role. Rules based on the Google Java Style Guide are applied, and a suppressions file can exempt specific classes.
Key checks:
- Naming rules (camelCase, CONSTANT_CASE)
- Import rules (no star imports, no unused imports)
- Block rules (mandatory braces, no empty blocks)
- Method length (50-line limit)
- Parameter count (7-parameter limit, excluding constructors)
Why Star Import (import .*) Is Prohibited
Why prohibit it?
Namespace Collision
If you star-import both java.util.Date and java.sql.Date, it becomes ambiguous which package Date refers to. The compiler may throw an error, or an unintended class could be used.
Unclear Dependencies
You cannot determine which classes are actually used just by looking at the code. This makes code reviews and debugging inconvenient.
Library Upgrade Risk
A new version of a library may introduce classes that conflict with existing class names in your code. Explicit imports prevent this risk.
Reference: Google Java Style Guide - Import statements
Exception: Static imports in test code are sometimes allowed for readability
Suppressions: Rules are relaxed for DTO, Entity, Config, and Test classes. These structurally tend to have many fields or lengthy configurations.
3. SpotBugs - Bug Detection
Role: Detect potential bug patterns
FindBugs has not been updated since 2015, so its successor SpotBugs was chosen. Google’s Error Prone (compile-time bug detection) was also considered, but its Gradle setup is complex and SpotBugs detects more bug patterns. Through bytecode analysis, it catches bugs that are hard to find from source code alone.
Types of bugs detected:
- Potential null pointer dereference
- Resource leaks (streams, connections)
- Concurrency issues
- Performance anti-patterns
- Security vulnerabilities
Configuration:
Exclude configuration: Warnings about DTO/Entity getters returning mutable objects (EI_EXPOSE_REP) were excluded since this is intentional behavior.
4. JaCoCo - Test Coverage
Role: Measure and verify code coverage
Cobertura has had slow updates since 2015, and IntelliJ’s built-in coverage can only be viewed within the IDE. JaCoCo is maintained by the Eclipse Foundation, quickly supports the latest Java versions, and integrates well with Gradle and Codecov, making it suitable for CI automation.
Coverage thresholds:
Why 60%/70%?
Below 40% means tests are virtually nonexistent. At 60%, core business logic is tested, which is a realistic goal for an early-stage project. At 80%, most code is tested and the project is in a stabilization phase. 100% requires testing even getters/setters, giving low ROI and being impractical.
Reference: Martin Fowler - Test Coverage
5. Codecov - Coverage Dashboard
Role: Visualize coverage and manage history
Coveralls also provides a free coverage dashboard, but Codecov has cleaner PR comments and easier GitHub Actions integration. SonarCloud is paid for private repos, and since individual tools were already in use, only a coverage dashboard was needed. Codecov is free for personal projects and works immediately upon uploading JaCoCo XML reports.
Codecov vs Coveralls Comparison

An important difference is visible in the image above. Codecov displays exact line counts rather than just percentages, and distinguishes between coverage changes outside the patch and code coverage within the patch.
Coveralls only shows whether coverage went up or down, making it feel like a numbers game. To verify whether the patch is fully covered, you have to visit the website directly. In contrast, Codecov lets you check detailed patch information right in the PR comment.
Source: Codecov vs Coveralls
Features provided by Codecov:
- Per-PR coverage change visualization
- Coverage trend graphs
- File/directory coverage map
- Slack/GitHub integration
Pricing:
- Public repos: Free
- Private repos (1-5 users): Free
- Private repos (6+ users): Paid plans
It is a private repo, but since I am the sole developer, it falls within the free tier.
Reference: Codecov Pricing
Setup steps:
- Connect GitHub at codecov.io
- Add
CODECOV_TOKENto Repository Settings > Secrets (token required for private repos) - Fine-tune settings with
codecov.yml
codecov.yml file location:
In a monorepo structure, codecov.yml must be placed at the repository root. Placing it in the backend/ folder will not be recognized.
- Allowed locations:
/,/dev/,/.github/ - Cannot be placed in subdirectories (e.g.,
/backend/)
Reference: Codecov YAML Reference
CI Pipeline Structure

Reasons for stage separation:
- Saves build time when code quality checks fail quickly
- Makes it clear which stage has the problem
Local Development Workflow
Pre-commit Checks
# Auto-apply formatting./gradlew spotlessApply
# Full check (same as CI)./gradlew checkRecommended IDE Setup
IntelliJ IDEA:
- File > Settings > Editor > Code Style > Java
- Click the gear icon next to Scheme > Import Scheme > Google Style
Key Gradle Tasks
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
spotlessCheck | Check formatting |
spotlessApply | Auto-apply formatting |
checkstyleMain | Checkstyle for main code |
checkstyleTest | Checkstyle for test code |
spotbugsMain | SpotBugs for main code |
test | Run tests |
jacocoTestReport | Generate coverage report |
jacocoTestCoverageVerification | Verify coverage thresholds |
check | Run all checks above |
Version Compatibility (Java 25 + Spring Boot 4)
| Tool | Version | Java 25 Support | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring Boot | 4.0.1 | Yes | Officially supports Java 17-25 |
| Spotless | 7.0.2 | Yes | Google Java Format |
| Checkstyle | 12.3.0 | Yes | 10.x only supports up to Java 22 |
| SpotBugs Plugin | 6.4.8 | Yes | 6.0.x does not support Java 25 |
| SpotBugs Annotations | 4.9.8 | Yes | |
| JaCoCo | 0.8.14 | Yes | 0.8.12 only supports up to Java 22 |
You must use the versions listed above or higher to use Java 25 LTS.
Cost Summary
| Tool | Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Spotless | Free | Gradle plugin |
| Checkstyle | Free | Built into Gradle |
| SpotBugs | Free | Gradle plugin |
| JaCoCo | Free | Built into Gradle |
| Codecov | Free | Free for individuals/open-source |
| GitHub Actions | Free | 2000 min/month for private repos |
Total cost: $0
